The basics of business intelligence dashboards
Business intelligence (BI) has continued to play an important role in business decision-making across all industries. BI uses a technology-driven method to track metrics about the firm, the customer, and the market. In simple terms, BI is all about utilizing the data generated by your company’s many operations and sectors. This information is then analyzed and presented to you to help you understand and obtain vital insights into how your company is doing. As a result of these actionable insights, you’ll be able to make more educated and intelligent business decisions that will help your company adapt and grow.
The amount of data generated every day in today’s modern corporate world is simply amazing. Without having to look at numerous reports, business intelligence enables firms to gain a complete overview of their business performance. Business intelligence tools enable you to display your data in a way that is readable, understandable, and edible.
What is a Business Intelligence Dashboard?
A business intelligence (BI) dashboard is a tool that visually presents data through charts, graphs, and key metrics, helping users analyze and report on business performance. BI dashboards consolidate information from multiple sources, allowing executives, managers, and teams to monitor KPIs and make informed decisions.
Would you prefer it if data was presented to you in dull Excel spreadsheets or through interactive, visually appealing dashboards?
Because the human mind is physiologically wired to interpret visuals better than simple text and numbers, it is likely that you would choose the second option. Effective data visualization is essential to understand your data.
Like a car dashboard that shows speed, fuel level, and even outside temperature, a BI dashboard shows a glimpse of your company’s performance. Your business measurements, KPIs, and other essential data points for decision-making can all be displayed in a BI dashboard. Monitoring and benchmarking the KPIs can help you assess the performance of your organization and identify areas that may require additional attention or inquiry.
BI dashboards are an important aspect of any business intelligence strategy. They should be designed and created specifically for analyzing data from diverse sources to expedite the decision-making process. Users can develop dynamic web-based dashboards to evaluate, present, and exchange data with internal and external stakeholders. BI dashboards are simply an interactive approach to visualizing different kinds of data for business purposes.
How Does a BI Dashboard Function?
BI dashboards offer businesses a powerful, visual tool to track performance, analyze data, and share insights seamlessly. By consolidating information from multiple sources into a single, interactive interface, they empower executives, managers, and teams to make well-informed decisions with ease.
How BI Dashboards Work:
- Data Integration: BI dashboards connect to various data sources, including databases, cloud storage, and data warehouses, ensuring comprehensive access to information.
- Data Transformation: Raw data is processed and presented as clear visual reports, graphs, and key performance indicators (KPIs), making complex insights easy to understand.
- Customization: Dashboards can be tailored to spotlight the metrics most relevant to specific business objectives or team goals.
- Drill-Down Functionality: Users can delve deeper into high-level data, uncovering detailed insights to inform strategic decisions.
- Collaboration & Sharing: Dashboards and reports can be easily shared, fostering better communication, alignment, and teamwork across an organization.
By streamlining data analysis and visualization, BI dashboards enable businesses to monitor performance in real time, respond to changing trends, and stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Features and components of a BI dashboard
BI dashboards are a technology-driven technique for analyzing and visualizing data in a straightforward manner. BI dashboards are a collection of charts and graphs that give viewers a 360-degree perspective of a company’s performance. Business users can utilize BI dashboards to get a consolidated view of crucial and connected KPIs and patterns for better decision-making and tactical planning.
BI dashboard solutions come with several features that may be utilized to automate tasks and enhance usability and aesthetic appeal.
Customizable and interactive interface: The customizable interface allows users to create a dashboard that meets their requirements. BI reports are more dynamic than static Excel reports because they draw data in real time directly from the sources.
Built-in standard dashboard templates: Templates speed up the creation process and increase aesthetic appeal by facilitating the organization of visualizations within dashboards.
Data source connections: BI dashboards can connect to data lakes, data warehouses, data marts, and other data sources to consolidate data for analysis.
Data visualizations: Users can use a variety of data visualization charts to illustrate different performance measures, ranging from simple line and bar charts to more complicated graphs like scatterplots and heatmaps.
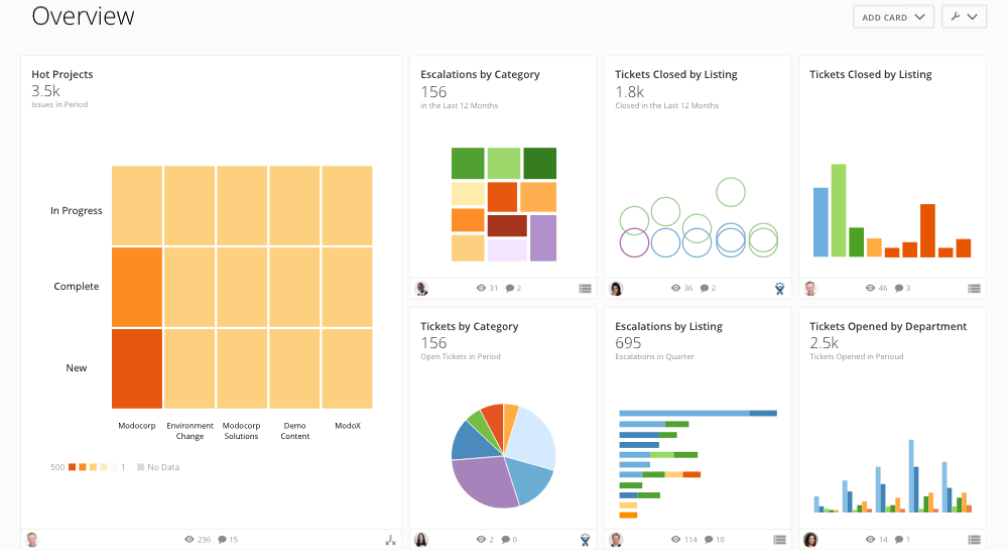
Drill-down capabilities: By clicking on a data visualization, users may get a closer look at a more detailed version of the data. This grants consumers access to extra visualizations or data tables, which are typically organized in a hierarchical structure that allows them to go down numerous levels.
Data filters: Data filtering capabilities within visualizations enable users to specify geographical settings, date and time ranges, and other characteristics to receive a more complete perspective of the processed data.
Tooltips and text boxes: Dashboards frequently feature pop-up information tooltips and standalone text boxes that clarify visible data and provide further context regarding analytics results.
Sharing capability: BI dashboards make it easy to share the findings of your research with others. This guarantees that knowledge is disseminated throughout the organization, encouraging collaboration.
All of these characteristics result in long-term benefits for BI dashboard users and the enterprise as a whole.
Types of BI Dashboards
Business intelligence (BI) dashboards come in various types, each tailored to meet specific business needs. Selecting the right dashboard depends on the data you need to monitor and how you intend to use it. Here’s a breakdown of the key types:
- Operational Dashboards – Designed for real-time monitoring of day-to-day processes and activities. For instance, a retail manager might rely on an operational dashboard to oversee inventory levels and track sales performance.
- Strategic Dashboards – These provide a high-level overview of business performance, enabling executives and decision-makers to identify trends, spot opportunities, and address challenges.
- Analytical Dashboards – Perfect for diving deep into data, analytical dashboards uncover patterns and correlations that support long-term strategies and forecasting.
- Sales Dashboards – Focused on tracking sales performance, revenue trends, and pipeline progress. They help sales teams monitor goals and pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Marketing Dashboards – Highlight key metrics like campaign performance, customer acquisition costs, and engagement levels, enabling marketers to refine their strategies effectively.
- Finance Dashboards – Vital for finance teams, these dashboards analyze budgets, monitor expenses, and assess overall financial health with up-to-date data.
Understanding these dashboard types allows businesses to choose the right tool to monitor critical metrics, enhance performance, and drive data-informed decisions with confidence.
Benefits and drawbacks of a business intelligence dashboard
BI dashboards have proven their worth to users of all kinds in a variety of situations. Technical users can deal with the data beneath the dashboard to create custom queries or do data-level filtering. Non-technical users can also interact with the dashboard by exploring the visualizations at the dashboard level. In summary, regardless of their technical expertise, any end user can stay up to date with data, analytical measurements, and KPIs.
Advantages of a BI dashboard
- Trend identification: Dashboards give business users the ability to spot and analyze promising trends, isolate and remedy bad trends, and provide forecast insight.
- Improved communication: The wonderful thing about BI dashboards is that they are simple to share with clients, colleagues, and any other important internal or external stakeholders to drive cooperation.
- Accurate forecasting: Finding patterns and trends by analyzing historical and present data is possible. Predictive analytics algorithms can also provide you with a glimpse into the future by forecasting key factors.
- Real-time insights: You must stay current on KPIs and other important measures in order to make informed and precise judgments. BI dashboards provide you with the most up-to-date and relevant data in real time. When BI tools allow you to update everything with only a few clicks, there’s no need to manually dig through endless databases to find what you’re looking for.
- Freedom and flexibility: The centralized and entirely portable nature of BI dashboards allows users to view and analyze data from a variety of devices, including a smartphone, desktop, laptop, or other device, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Drawbacks of a BI dashboard
- Bad designs: Dashboard designs that are overly bright and cluttered might be difficult to understand and use.
- Difficult to use: Drill-down methods to probe the data beneath surface metrics are sometimes challenging for BI users to create.
- Expensive: Some BI dashboard tools are costly and are targeted at larger enterprises.

How to Create a Business Intelligence Dashboard
Designing a business intelligence (BI) dashboard is about more than gathering data—it’s about crafting a tool that delivers meaningful, actionable insights. To create an effective BI dashboard, consider these essential best practices:
- Define Your Goals:
Begin by clearly outlining the business objectives you aim to analyze, measure, and improve. Are you seeking to uncover new market opportunities or refine a specific stage of your marketing funnel? Defining your goals upfront will provide clarity and direction, ensuring the data you gather and present is both relevant and actionable. - Integrate Your Data:
To build an effective dashboard, start by ensuring your data is clean and analysis-ready. This process involves gathering data from various sources, standardizing it into a consistent format, and storing it in a centralized system like a data warehouse or data lake. By integrating your data properly, you gain a complete and accurate view of your business performance. - Focus on the Most Important Reporting Requirements:
Always consider your end users and decision-makers. Present only the most relevant data, thoughtfully tailored to align with their needs, capabilities, and goals. By doing so, you can prioritize what information to showcase, creating a dashboard that is not only practical but also engaging and impactful. - Include All Relevant Information and Context:
Context is essential when presenting data. Stakeholders need to understand trends without overlooking critical details. Ensure your dashboard offers a comprehensive view by emphasizing the factors that drive your key metrics, making complex information clear and actionable. - Highlight KPIs and Create an Engaging Story:
Leverage your data to craft a compelling and unified narrative. Present key performance indicators (KPIs) in a way that captures attention and motivates action. The aim is to make your insights both informative and engaging, leaving a lasting impression on your audience. - Present Accurate Data That Prompts Action:
The primary goal of a dashboard is to empower stakeholders to make informed decisions. To achieve this, the data it displays must be both accurate and actionable. Clear, well-structured data that is directly linked to specific actions enables decision-makers to respond decisively and with confidence. - Keep Visuals Clean and Simple:
A cluttered dashboard can be hard to understand. To effectively convey your data story, select charts, graphs, and visual elements that prioritize clarity without overwhelming the audience. By focusing on simplicity and intuitive design, you can create a dashboard that is both easy to navigate and effortless to interpret. - Allow Exploration and Collaboration:
The most effective BI dashboards empower users to independently explore and analyze data. Prioritize self-service features that allow users to drill down and uncover insights on their own terms. Opt for tools equipped with an associative engine, enabling seamless exploration of data connections without being restricted to linear queries. - Leverage AI and Augmented Analytics:
Modern BI dashboards now incorporate augmented analytics, leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to uncover insights and perform advanced analyses. These technologies enhance human intuition, simplifying the process of identifying hidden trends and anomalies. With features like AI-powered recommendations and natural language search, these dashboards are more intuitive, user-friendly, and insightful than ever before. - Avoid Clutter:
A BI dashboard should strike a balance between visual appeal and simplicity. Avoid cluttering the interface with excessive graphic elements that may overwhelm users. Instead, prioritize a clean, streamlined design that emphasizes key metrics, ensuring the data remains clear and free from unnecessary distractions.
Conclusion
Informed decision-making drives opportunities, innovation, and success. BI dashboards empower organizations by sharing critical insights, enabling individuals at every level to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Check out some related resources:

Elevate Your Organization's Data-Driven Culture with Strong Governance Practices

10 Qlik Alternatives & Competitors in 2025